Available in Stock & Ready to Ship
Wafer identification (ID) is essential for wafer fabrication. Wafer ID can be used to associate production-process data in a manufacture-execution system, which helps product-quality tracing. High-end Wafer ID Readers for single wafer tracking by reading the ID codes like Barcodes, OCR Codes (optical characterization), Datamatrix codes or QR Codes. Additionally, we also offer Batch Wafer Reader and automatic Wafer Alignment (notch).
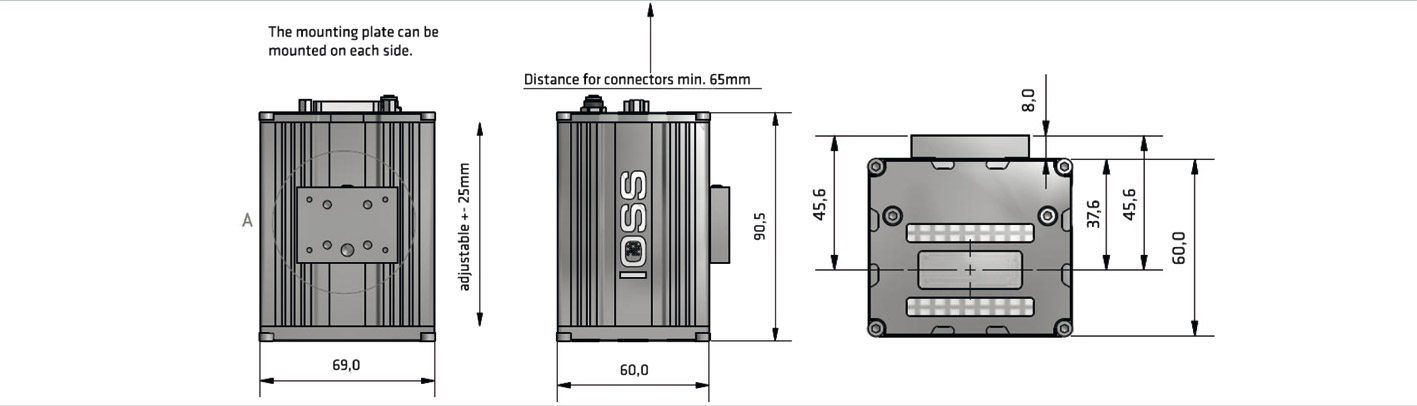
Features of the Semiconductor Wafer ID Reader, WID120:
- Revolutionary integrated RGB illumination
- Fully automatic exposure control
- Code shift compensation
- High and fast reading rates
- Intelligent configurations handling
- Precise fine-tuning
- Additional external RGB light source
Benefits of the Semiconductor Wafer ID Reader, WID120:
- OCR, Barcode, DataMatrix and QR code
- Easy graphical user interface, w/ teach-in wizard
- Easy integration
- Best Cost of Ownership:
- Achieve the highest yield
- Increase of MTBA/MTBF
- Decrease of MTTR
READING CAPABILITY
- Mark type SEMI M12, M13, M1.15,SEMI T1.95
- OCR fonts SEMI FONT (straight, concave and convex), NON-SEMI FONTS
- 2D codes ECC200, T7 Data Matrix, QR Code and M1.15
- Barcodes BC412/IBM412,IBM & SEMI T1-95, Base 35
- Region of Interest Flexible auto-catching ROI
ILLUMINATION AND OPTICS
- Field of view 35×13mm, Ultra-wide field of view
- LED Multi-channel RGB (Red/Green/Blue) – 440-480nm (Blue) – 500-555 (Green) – 620-650nm (Red)
- Object wafer: OCR Font, DataMatrix, T7, QR Code, Barcode on any wafer surface
- Light mode: 15 internal external (3 colors-RGB) + 3 additional external RGB source
- Intensity of illumination: Variable with automatic exposure controller – Dynamic Range 1: 10,000
- Lens type: Aspheric lens (made in Germany) with bandwidth pass filter
- Depth of focus: ±4mm
COMMUNICATION I/O
- Network: 10/100Base-T Ethernet port ×1, TCP/IP protocol
- Serial: RS-232C
- Protocol: C Library, LKx5 Protocol, TEL Protocol, TSK Protocol, EG Protocol and customized
- Discrete input/output: Included 2 Input + 2 Output
- Status indicator: LED Status + LED Power
- Master/Slave: For automatic front and backside reading
- Database feature: Direct database connection for result crosscheck or manipulation
CERTIFICATES
Compliance regulation: CE, RoHS, FCC